Getting Dual Citizenship: Your Roadmap to Freedom and Opportunities
Navigating the path to getting dual citizenship can be straightforward with the right information. Whether you are led by heritage, residence, or other ties, this guide sheds light on the essential steps, from eligibility criteria to potential challenges, helping you unlock the doors to dual nationality.
Key Takeaways
- Dual citizenship is recognized differently by nations with some allowing it, others imposing restrictions, and some not recognizing it at all, making the associated rights and obligations vary.
- There are various pathways to obtaining dual citizenship, including birthright, ancestry, marriage, naturalization and investment, each with their own specific documentation and eligibility criteria.
- While dual citizenship can offer significant advantages such as travel freedom and economic opportunities, it also comes with challenges like complex tax implications and possible military service obligations in both countries.
Understanding Dual Citizenship

Dual citizenship refers to the concurrent citizenship of an individual in two different countries. It’s a legal status where an individual is recognized as a citizen of two countries, enjoying the rights and fulfilling the obligations of both nations. The availability of dual citizenship, however, is not universal. The countries involved play a decisive role – some might offer the option, while others may not recognize it at all.
Dual citizens, or dual nationals, have the advantage of enjoying the privileges of citizenship in both countries they are a part of. As a dual national, this might include the right to vote, work, and receive public benefits. But it’s not all rosy. Dual citizens also shoulder any obligations that citizenship in each country entails. This could mean paying taxes, serving in the military, or abiding by specific laws.
Dual Citizenship vs. Multiple Citizenship
While dual citizenship involves holding official passports from two countries, with both nations recognizing the individual’s rights and obligations, the concept of multiple citizenship extends this to more than two nations. In the scenario of multiple citizenship, however, each country generally views the individual as its sole citizen, lacking a formal mutual recognition system among the nations. So, while you might hear terms like ‘triple citizenship,’ they are not officially recognized in legislative terminology.
Individuals possessing three or more citizenships are typically considered to have dual or second citizenship.
Dual Citizenship: Country Overview
The world of dual citizenship is as diverse as the globe itself, with each country carrying its unique set of rules and requirements. Some countries welcome dual citizens with open arms, while others impose strict restrictions or don’t allow dual citizenship at all. Understanding the specific requirements of the countries you’re interested in is crucial before you commence your journey towards dual citizenship.
Even though dual citizenship appeals to many, its acceptance is not universal. Approximately 49% of all countries around the world permit dual citizenship, with some countries imposing specific conditions.

Countries That Allow Dual Citizenship: Europe
Many European countries permit dual citizenship, allowing individuals to hold citizenship in more than one country simultaneously. Here are some examples of countries that of European countries that allow dual citizenship:

It’s important to note that the rules and conditions for obtaining dual citizenship can vary significantly from one country to another. Some countries may offer citizenship by descent, naturalization, marriage, or through investment programs. Individuals interested in acquiring dual citizenship should consult with experts or lawyers to understand the specific requirements and processes for the country in question.
Dual citizenship in other countries
Dual citizenship policies vary across the globe, with some countries offering a more straightforward path to obtaining it. Here’s a look at the dual citizenship policies of the countries mentioned:
Many people consider obtaining dual citizenship in a foreign country, as some are known for their comparatively straightforward dual citizenship policies. However, each of these countries has its unique requirements and processes, which highlights the importance of comprehensive research and preparation.
Countries with Flexible Dual Citizenship Policies
Countries with flexible dual citizenship policies are often the most appealing to prospective dual citizens. Several European Union countries maintain lenient policies and allow dual nationality, for example: Cyprus, Greece, Italy, Poland, Sweden, Portugal, France and Hungary.
Portugal and Italy are particularly lenient, facilitating the acquisition of dual citizenship. Additionally, Malta offers a route to dual citizenship for reputable investors who meet certain requirements, including a minimum investment.
Countries with Strict Dual Citizenship Policies
Conversely, some countries adhere to strict policies against dual citizenship. Countries that do not allow their citizens to hold dual citizenship include: India, China, Afghanistan, Azerbaijan and Bahrain.
Also Germany allow dual citizenship only in certain cases, such as the impossibility of giving up your previous nationality (e.g. if that country does not allow the renouncement of citizenship or if giving up previous nationality would result in major financial loss). Germany bans dual citizenship for individuals over 18 years old.
Additionally, Austria allows individuals to maintain their former citizenship in certain cases, such as when another citizenship is acquired at birth through a parent or birthplace. However, Austria generally does not recognize dual citizenship for those acquiring citizenship through investment, except under special provisions.
On the other hand, Turkey allows Turkey dual citizenship, but does not allow multiple citizenship.
Moreover, certain countries like Croatia, Bulgaria, India, Pakistan, and Panama allow for dual citizenship, including British citizenship, under specific conditions or for specific groups of people, such as ethnic descendants or those with a foreign nationality.
Meanwhile, countries like Spain, Latvia, and Lithuania generally only allow dual citizenship in exceptional cases. These restrictions often mean that individuals must choose between nationalities and potentially give up the benefits and rights offered by holding dual citizenship.
Benefits of Obtaining Dual Citizenship

Adopting dual citizenship can be equated to unveiling a wealth of opportunities and benefits spread across two countries. From eliminating legal restrictions on the ability to work or start a business in the second country to facilitating the freedom to travel, live, and access social benefits in both countries, the perks of obtaining dual citizenship are indeed enticing.
Furthermore, dual citizenship offers a platform for immersing oneself culturally and experiencing diverse educational opportunities.
Travel Freedom and Foreign Passports
Have you ever envisioned breezing through immigration lines or sidestepping the inconvenience of visa applications with each travel? If so, dual citizenship could be your golden ticket. Dual citizens can carry passports from both countries, simplifying travel and entry between them. This also means they can select the passport that offers the easiest entry to their destination, further streamlining their travel arrangements.
Furthermore, dual citizens relish the privilege of unrestricted, visa-free travel to countries of their citizenship, thereby enabling them to stay for prolonged durations without limitations. They can also leverage visa-free agreements of each country, expanding their travel opportunities to various regions including the UK, Singapore, and the European Schengen zone. In essence, dual citizenship guarantees individuals the essential freedom of movement needed for work and personal life.
Job Opportunities and Economic Advantages
Dual citizenship is much more than a travel pass; it’s a key to unlock a world of professional and economic opportunities. As a dual citizen, you can seek employment in both countries without needing a work permit that foreign nationals typically must obtain. This can open up a wealth of job opportunities that might not be accessible otherwise.
Moreover, being a dual citizen can enhance your business prospects by providing access to two markets. This enables you to participate in economic activities without the limitations imposed on foreign business entities. And if you’re an entrepreneur or investor, countries like Turkey and Caribbean nations offer citizenship through investment programs, providing a straightforward path for those looking to expand their business interests.
Additionally, a second passport, often referred to as a foreign passport, obtained through dual citizenship can provide the following benefits:
- Ease the process of securing advanced travel visas for work or business-related travel
- Grant you access to more favorable business environments
- Access to stable economies
- Beneficial tax systems
- Government support for startups, especially in regions such as the European Union.
Challenges and Considerations

Despite the plethora of benefits, dual citizenship also brings along its unique set of challenges and considerations. From potential barriers in employment sectors to navigating conflicting legal obligations, dual citizenship can pose certain complexities.
For instance, some sectors that require strict security clearance may raise concerns of dual loyalty and foreign influence, potentially restricting job opportunities. Dual citizens are also subject to the laws of both countries, which can impact their rights to hold public office, vote, or access government jobs in certain nations. Moreover, specific countries might impose distinct travel and residency prerequisites for dual citizens.
Taxation and Financial Implications
The realm of taxation presents one of the major challenges of dual citizenship. Dual citizens are often subject to the tax laws of both countries. This can potentially lead to a situation of double taxation, where the same income is taxed in both countries. However, fear not! To mitigate such instances, tax treaties exist between many countries. Dual citizens can utilize the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion and the Foreign Tax Credit to decrease their tax burden on income earned abroad.
Furthermore, strategic planning can help dual citizens navigate the complex tax landscape. For instance, dual citizens have the ability to:
- strategically choose their country of tax residency
- position themselves in a more tax-favorable jurisdiction to potentially reduce their overall tax liability
- take advantage of beneficial tax regimes offered by some countries, such as exemptions from income, capital gains, or inheritance taxes
However, staying informed about the complexities of tax laws and reporting requirements is crucial.
Military Service Obligations
Military service obligations pose another potential challenge for dual citizens. In many countries, citizenship comes with a duty to serve in the military. As a dual citizen, you may have military service obligations in both countries of your citizenship and must comply with the legislation of both nations.
However, there are exceptions. Some countries may exempt you from military obligations if you’re most closely connected to that country. Also, a few countries have specific laws regarding military service for dual nationals.
Eligibility Criteria for Dual Citizenship
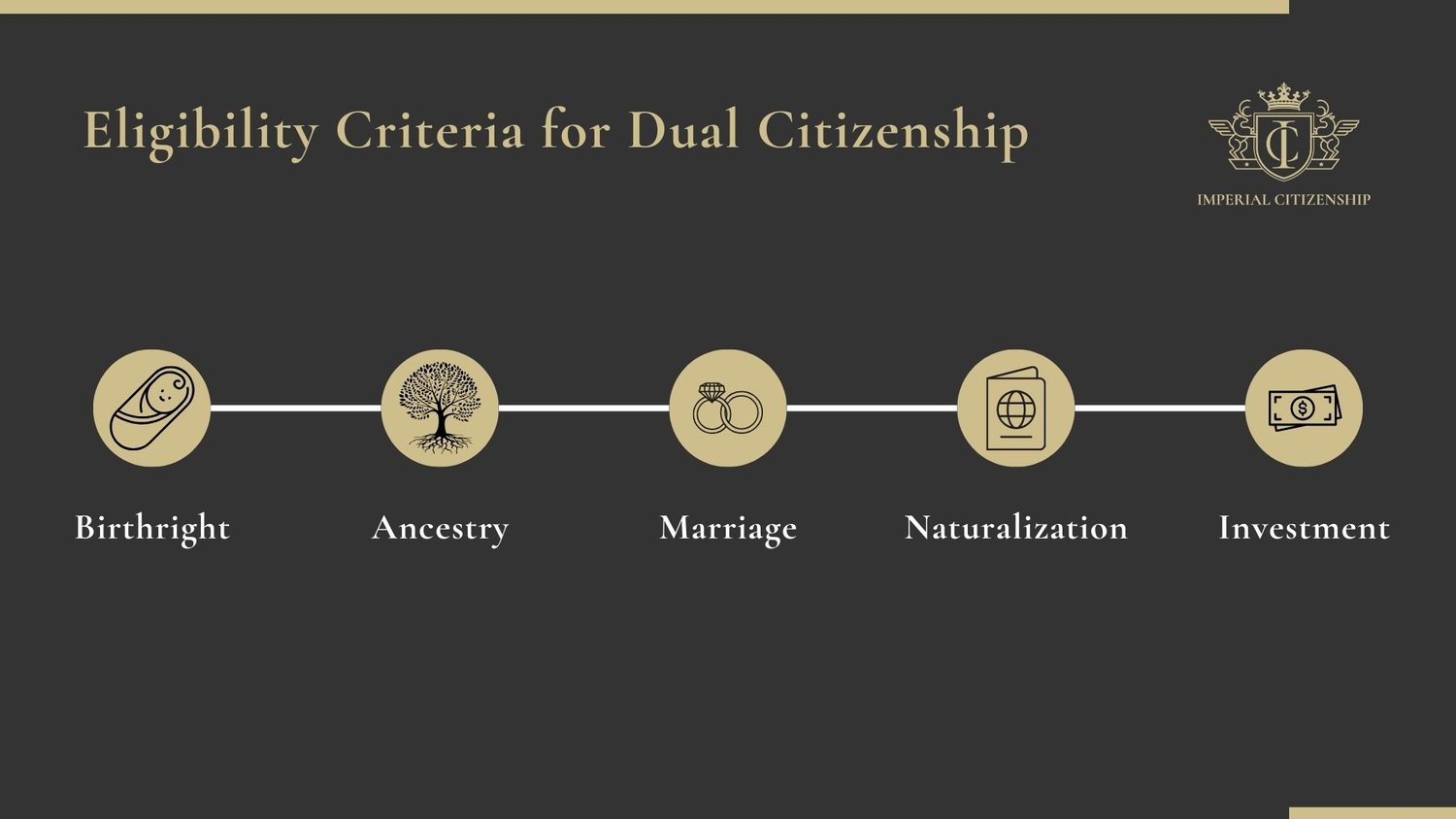
How can one attain dual citizenship? The eligibility criteria for dual citizenship vary by country and can be based on:
- Birthright
- Ancestry
- Marriage
- Naturalization
- Investment
Some countries may require individuals to renounce their current citizenship, while others allow dual citizenship if obligations to both nations are fulfilled.
Even in the absence of official recognition of dual citizenship by a country, possibilities to acquire citizenship in more than one country might still exist. Certain countries might also require proof, such as a government-issued document from the other country, to ensure there are no legal restrictions preventing an individual from holding dual citizenship.
Birthright Citizenship
Birthright citizenship, anchored in the principle of jus soli, bestows citizenship based on the location of birth. In countries such as Spain, anyone born on the country’s soil is automatically granted citizenship, irrespective of their parents’ citizenship status.
Ancestry and Heritage
Your lineage could be your ticket to dual citizenship. Citizenship by ancestry or descent allows individuals to become citizens of a country if they have ancestors who were citizens of that country. However, each country has distinct requirements for citizenship by ancestry, often involving proving lineage through documentation.
Interestingly, countries across all continents recognize citizenship by ancestry. This includes various countries in:
- Africa like Cape Verde and Kenya
- Americas like Argentina and Mexico
- Asia such as Mongolia and Singapore
- Europe including Austria and France
- Middle East like Bahrain and Jordan
- Oceania like Australia and New Zealand
Marriage and Family Ties
Love can indeed cross borders, and in some cases, it can even grant you citizenship in another country. Many countries offer expedited naturalization for spouses of citizens, making marriage a viable path to dual citizenship.
However, just like other paths to dual citizenship, to obtain citizenship through marriage or family ties requires proper documentation. Applicants typically need to provide documents:
- Marriage certificates
- Birth certificates or consular birth certificates
- Citizenship certificates for a spouse or unmarried children under a certain age.
Naturalization Process
The naturalization process forms another key route to dual citizenship. However, this process varies by country and is governed by each nation’s laws and policies. Some countries may have residency requirements or require demonstration of cultural, linguistic, or civic knowledge for naturalization.
The process may involve several stages, including submitting a formal application, attending interviews, and participating in a naturalization ceremony if required by the host country. Certain categories of dual citizenship like professional or financial investment categories may require additional documents such as educational or professional certificates, proof of owning assets, or bank confirmation letters.
Citizenship by Investment Program
Investment-based citizenship programs, like those offered by certain Caribbean countries, provide a unique pathway to dual citizenship. These programs often require substantial financial investments, typically in the form of contributions to a country’s development fund, real estate purchases, or other approved investment options.
Participating in a Citizenship by Investment Program (CIP) offers a myriad of benefits, making it an enticing option for global citizens seeking to broaden their citizenship portfolio:
- Global Mobility: Acquiring citizenship through investment often grants individuals visa-free or visa-on-arrival access to numerous countries, facilitating unrestricted global travel.
- Diversification of Assets: Real estate investments, contributions to development funds, or participation in specified investment projects not only contribute to the investor’s citizenship eligibility but also offer opportunities for asset diversification.
- Wealth Preservation: Investment-based citizenship provides a means to safeguard wealth and assets, especially in politically stable and economically resilient nations.
- Access to Educational Opportunities: Dual citizenship may open doors to educational institutions and programs in multiple countries, enhancing opportunities for personal and familial growth.
- Strategic Business Expansion: Holding citizenship in more than one country can be advantageous for international business endeavors, offering flexibility and strategic positioning in global markets.
- Tax Optimization: Certain countries with citizenship by investment programs provide favorable tax regimes, allowing individuals to optimize their tax liabilities.
- Family Security: Investment-based citizenship programs often extend benefits to the investor’s immediate family, including spouses, children, and sometimes even parents.
- Cultural and Social Inclusion: Dual citizenship can foster cultural exchange, social integration, and a sense of belonging in multiple communities, enriching the individual’s life experience.
It’s crucial for individuals considering participation in a Citizenship by Investment Program to conduct thorough research, understand the specific requirements of the chosen program, and seek professional guidance to navigate the complexities of dual citizenship acquisition. For more information, you can visit Imperial Citizenship.
Steps to Apply for Dual Citizenship

Now that you’re acquainted with the diverse routes to dual citizenship, let’s navigate through the overarching steps of its application. Obtaining dual citizenship can be a complex process that may necessitate the services of an immigration lawyer and help profesional firm specialized in support investors obtain a Second Citizenship or Residency through the means of investments. You’ll need to gather essential documents such as your birth certificate, passport, and marriage certificate if applicable.
Ultimately, you’ll need to traverse the naturalization process, which could involve multiple stages like submitting a formal application, attending interviews, and taking part in a naturalization ceremony, if required by the host country.
Gathering Documentation
The journey towards dual citizenship commences with the gathering of necessary documentation. These documents serve as proof of your identity, residency, and eligibility for dual citizenship. Typically, you’ll need to provide your birth certificate, marriage certificate if applicable, and proof of residency.
In some cases, you may need additional documents. For example, those resuming citizenship will require a certified copy of the foreign citizenship certificate and a police clearance report. If you’re applying for citizenship retention, proof of permanent residency and a police clearance report will be necessary.
Contacting Embassies and Consulates
Having collected all the necessary documents, the subsequent step involves reaching out to the relevant embassies or consulates. These bodies can provide you with accurate information and guidance on the dual citizenship application process. You can find their contact details on the official website of your government’s department or ministry responsible for foreign affairs.
Remember, you must submit your applications for dual citizenship either directly to the responsible department or through your country’s overseas missions. If you’re submitting documents through overseas missions, they must be authenticated by a senior officer of the mission. It’s advisable to reach out to the embassy or consulate via official email or phone numbers listed on their website to ensure the communication is recorded and reliable.
Completing the Naturalization Process
Completing the naturalization process marks the final stride towards attaining dual citizenship. This process might seem daunting at first, but with proper preparation, it can be a smooth journey. After submitting the naturalization application, you’ll need to pay a fee, which varies depending on your role in the application, such as the main applicant, spouse, or child.
Some countries may require an oath of allegiance or participation in a citizenship ceremony as a final step in the naturalization process, as outlined in their nationality act. This ceremony is a formal event where you officially become a citizen of your new country. It’s a significant milestone in your journey to dual citizenship, marking the end of your application process and the beginning of your new life as a dual citizen.
Summary
Having journeyed through the intricate world of dual citizenship, it’s clear that this unique status offers a myriad of benefits, from travel freedom and job opportunities to access to social benefits in two countries. However, it’s equally important to recognize the challenges and complexities involved in the process, including navigating complex tax laws, conflicting legal obligations, and country-specific regulations.
Dual citizenship is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and the journey towards it requires careful consideration, thorough research, and meticulous preparation. But for those who embark on this journey, dual citizenship can open doors to a world of opportunities, enriching your life in ways you never imagined.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I get dual citizenship?
You can acquire dual citizenship through birth, naturalization, marriage, or investment. Consider these options to obtain a second citizenship and passport.
How long can you have dual citizenship?
You can have dual citizenship indefinitely, as it never expires.
What is dual citizenship?
Dual citizenship is a legal status allowing an individual to be a citizen of two countries, with rights and obligations in both.
